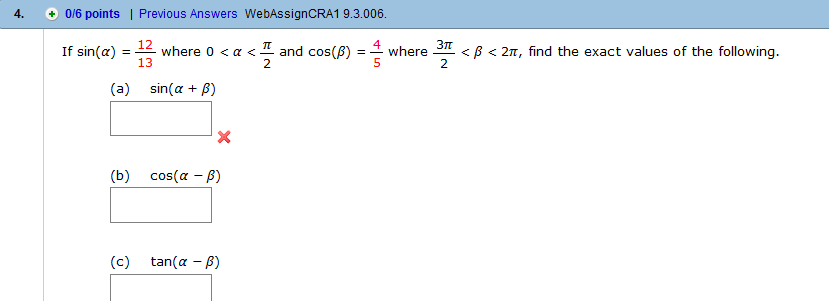
If sin A = 4/5,pi/2<A<pi and cos B = 5/13,3pi/2<B<2pi , find (i) sin (A + B) , (ii) cos (A - B) , (iii) tan (A - B)

SOLVED: 1. tan a = 8/15, pi < a < 3pi/2; cos b =-5/13, pi/2 < b Find sin(a+b) A) 140/221 B) 220/221 C) -220/221 D) 171/221 E) -21/221 F) -140/221 2.

SOLVED: Use range reduction express the following in terms of sin and cos of angles between 0 and pi/4. For example, sin((7/3)"pi) sin((1/3)*pi) cos((1/2-1/3)"pi) cos (pi/6) sin((17/8) *pi) sin((255/16)"pi) cos((931/13)* pi) Useful trig
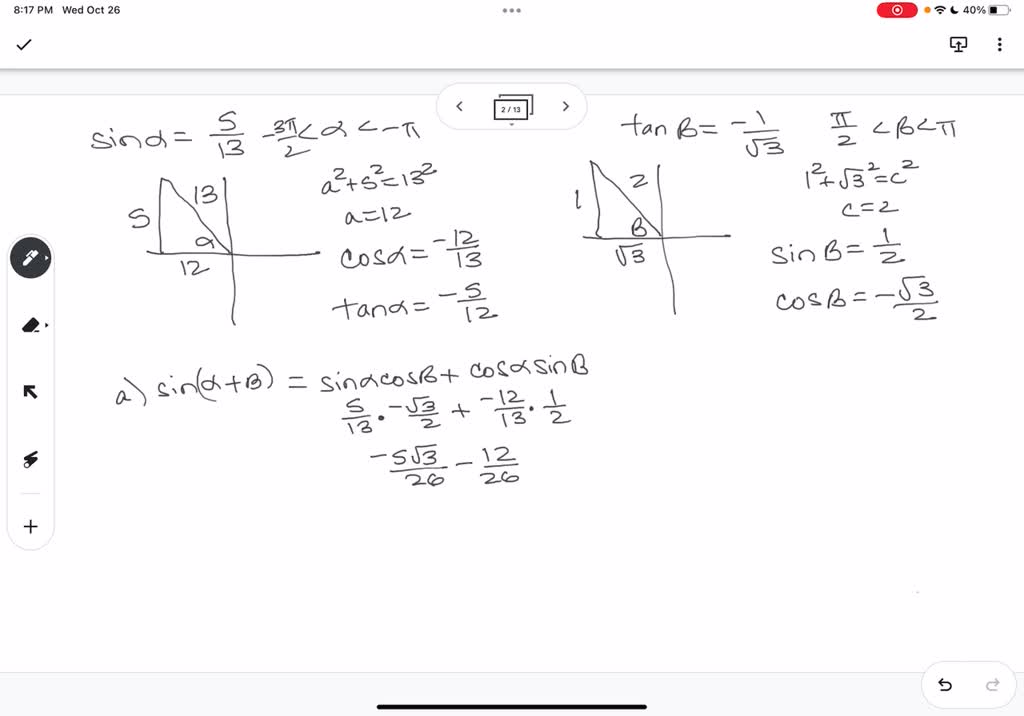
SOLVED: Find the exact value of each of the following under the given conditions below. (1) sin a (alpha) = 5/13 , -3pi/2 <a<-pi; tan (beta) = -1/ sqrt(3), pi/2<beta<pi a) sin (
Prove that 2cos(π/13)cos(9π/13) + cos(3π/13) + cos(5π/13) = 0 - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
Prove that: 2cos pi/13.cos 9pi/13 + cos 3pi/13 + cos 5pi/13 = 0 - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community