Discovery of Novel Adenosine Receptor Antagonists through a Combined Structure- and Ligand-Based Approach Followed by Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Ligand Binding Mode | Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling
No context available - how to use? Node 8.12.0 (and Typescript 3.3) · Issue #42 · Jeff-Lewis/cls-hooked · GitHub

The Mechanism of Action of Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators Can Be Predicted from Binding to Early Assembly Intermediates | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
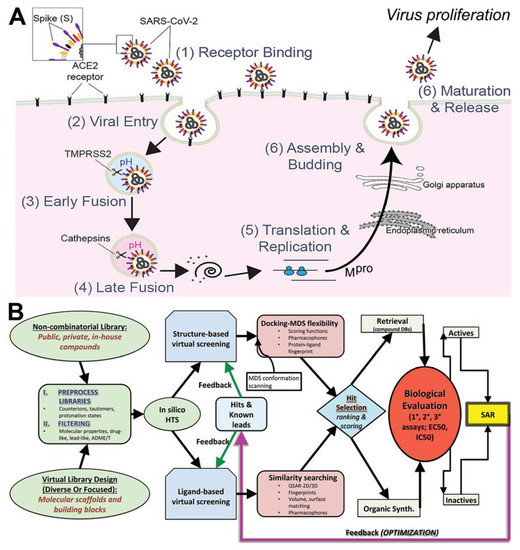
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Attacking COVID-19 Progression Using Multi-Drug Therapy for Synergetic Target Engagement

Hydrophobicity Determines the Bacterial Killing Rate of α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides and Influences the Bacterial Resistance Development | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Error: No context available. ns.run() or ns.bind() must be called first. · Issue #107 · RisingStack/trace-nodejs · GitHub

Integrating Biochar, Bacteria, and Plants for Sustainable Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Organic Pollutants | Environmental Science & Technology

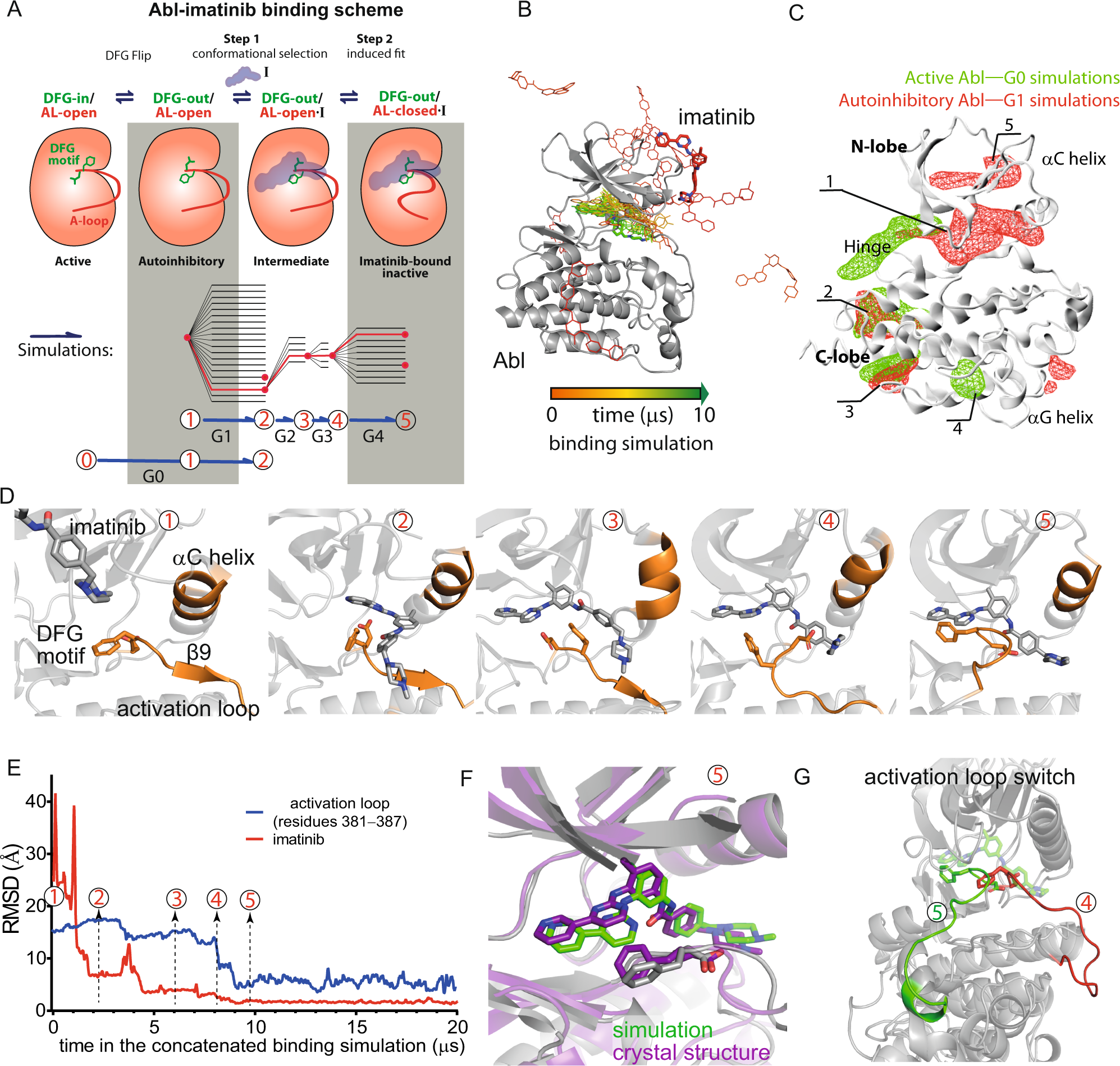
A molecular switch modulates assembly and host factor binding of the HIV-1 capsid | Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
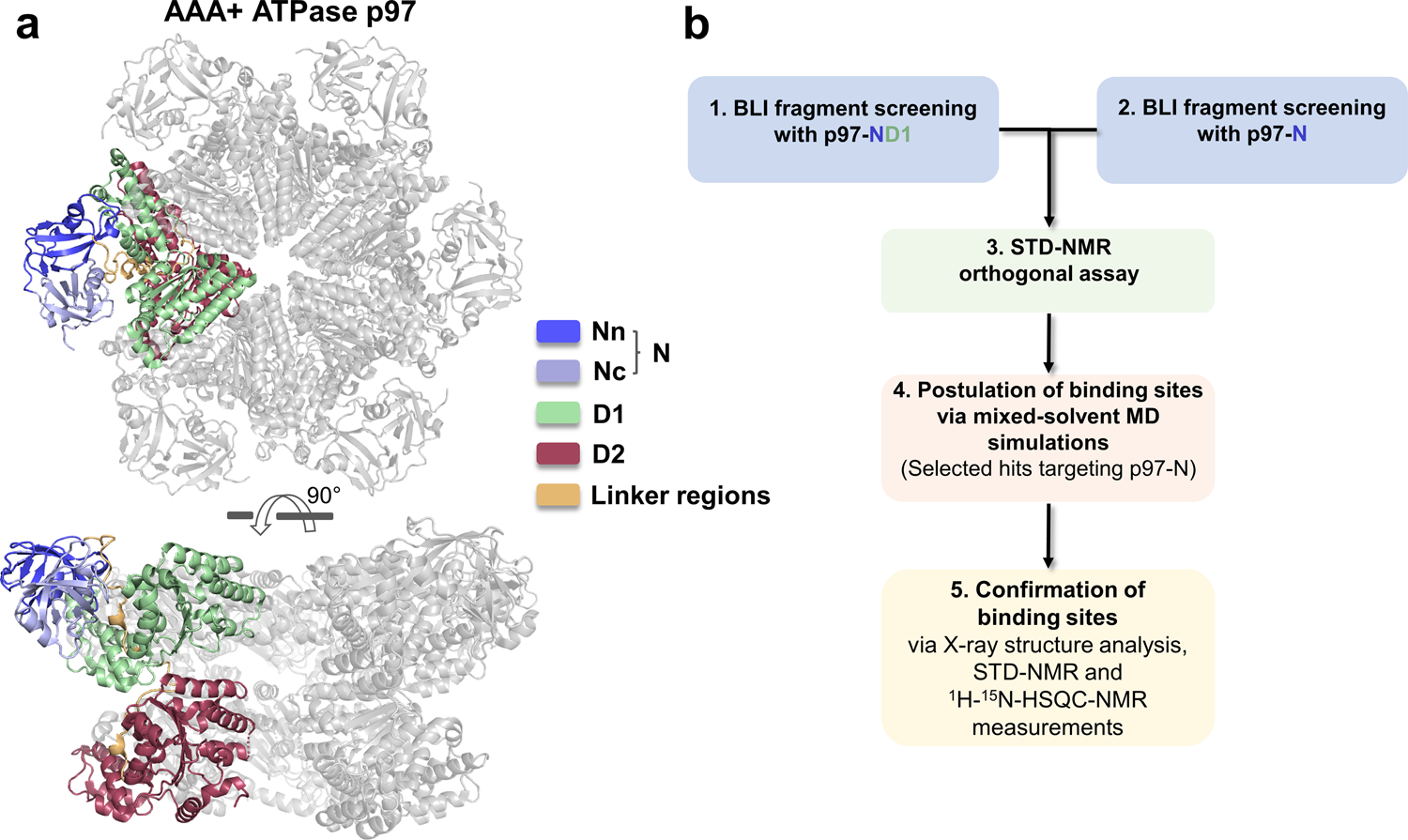
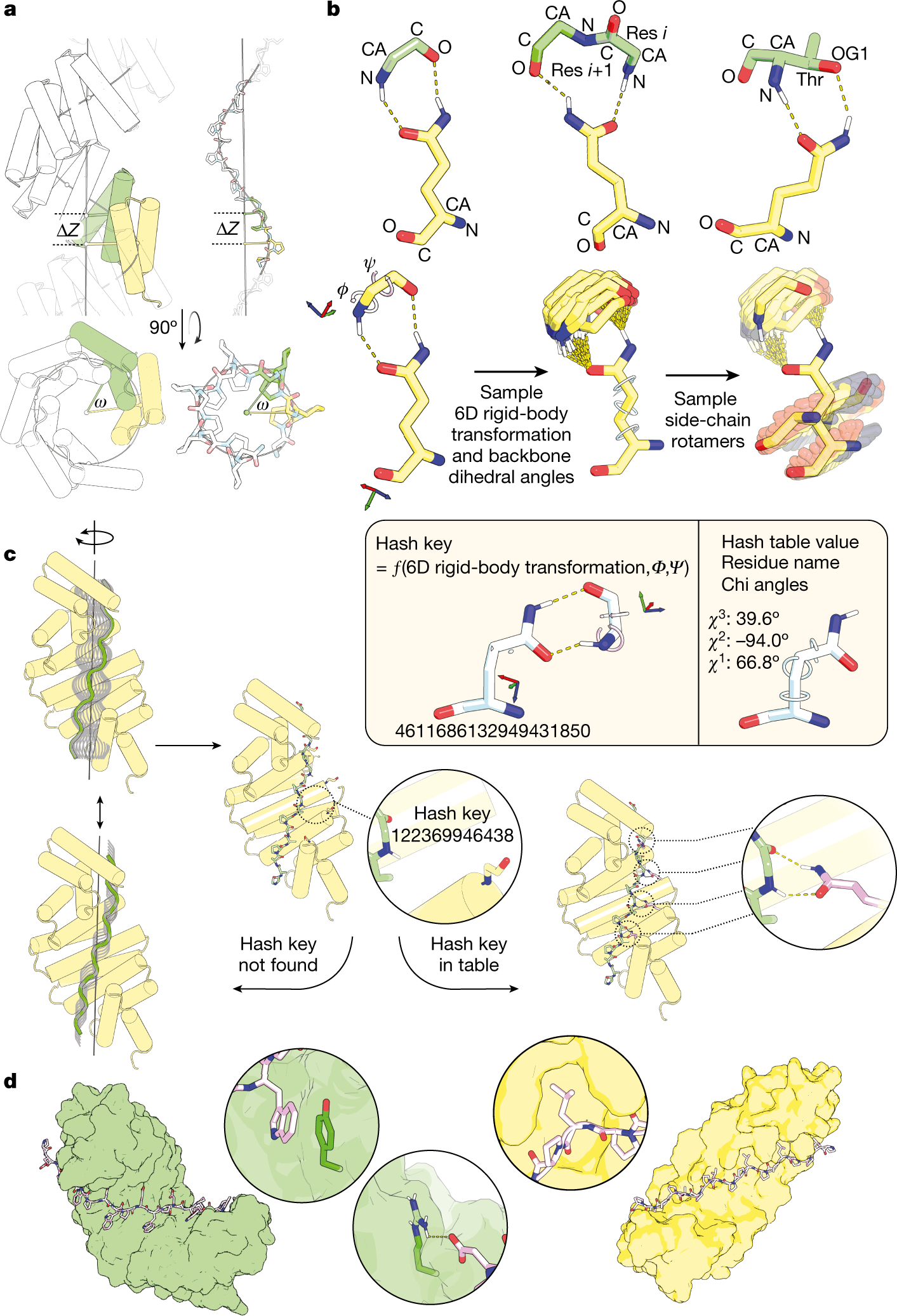
Fragment screening using biolayer interferometry reveals ligands targeting the SHP-motif binding site of the AAA+ ATPase p97 | Communications Chemistry
Error: No context available. ns.run() or ns.bind() must be called first. · Issue #59 · aws/aws-xray-sdk-node · GitHub

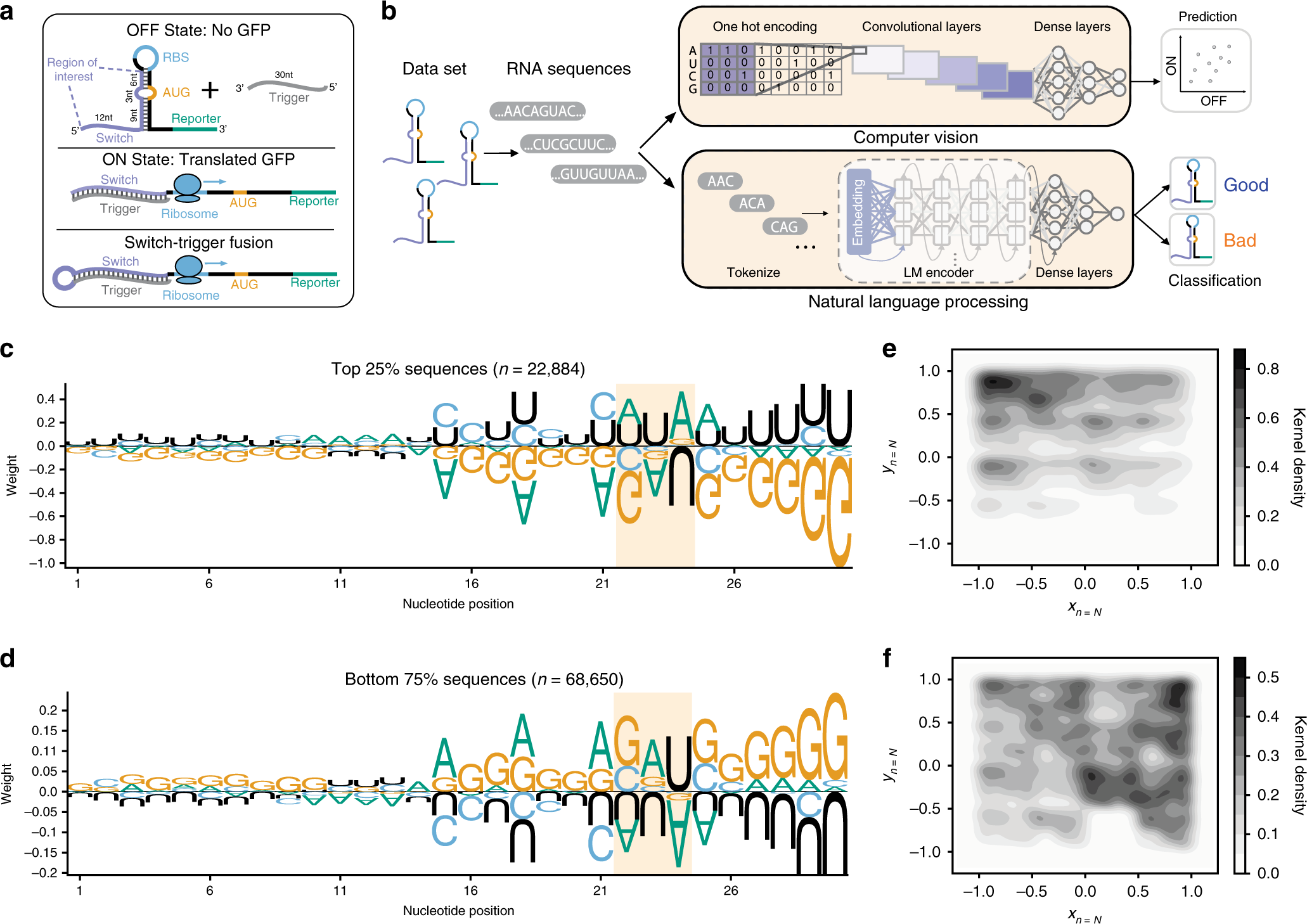
DNA Hairpins and Dumbbell-Wheel Transitions Amplified Walking Nanomachine for Ultrasensitive Nucleic Acid Detection | ACS Nano
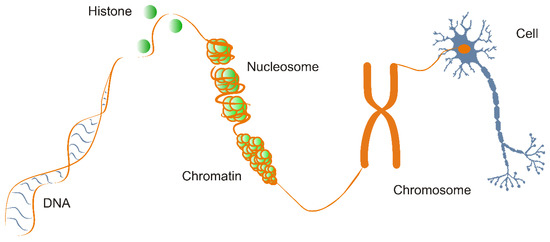
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Molecular Structure, Binding Affinity, and Biological Activity in the Epigenome
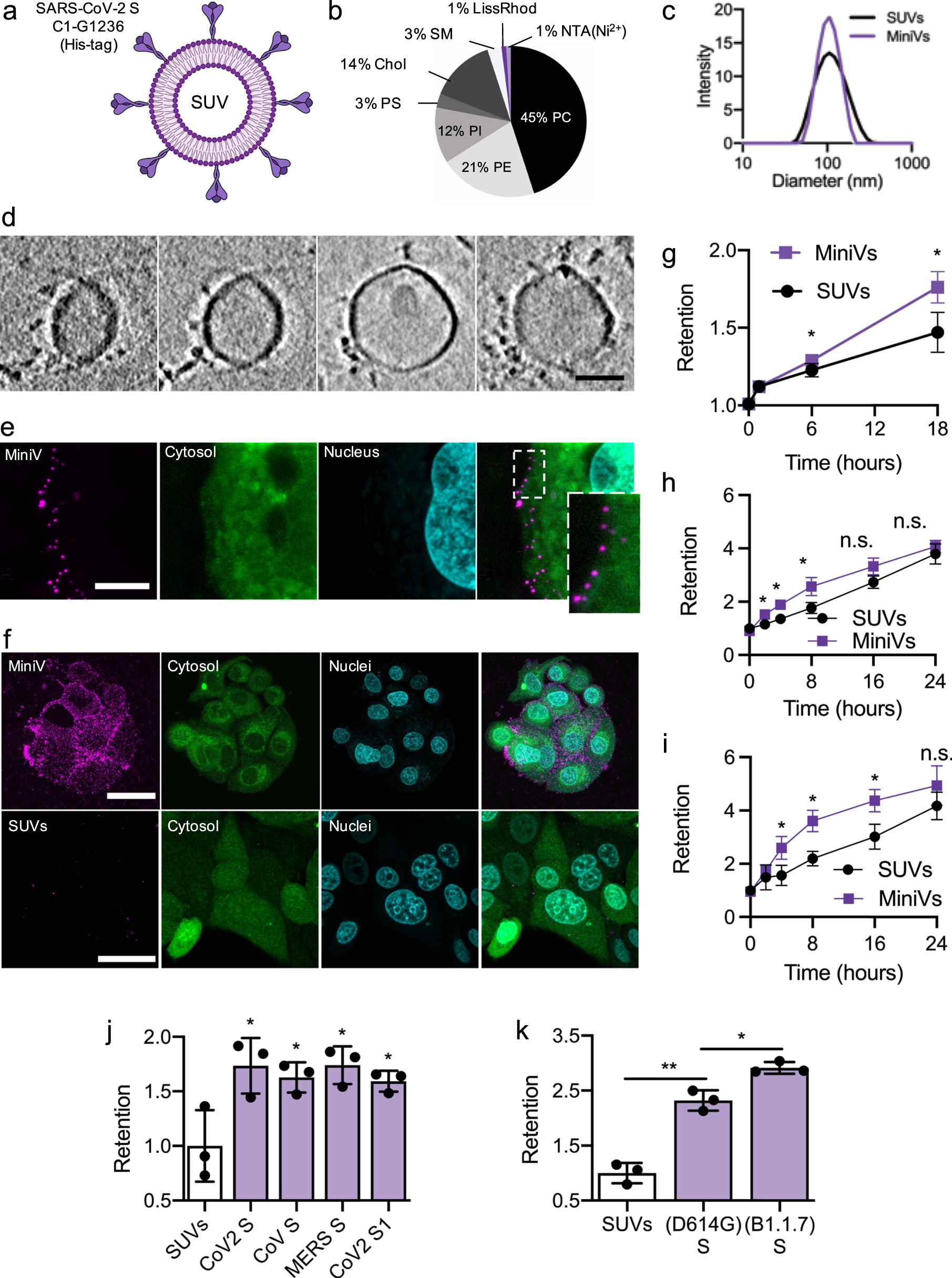
Synthetic virions reveal fatty acid-coupled adaptive immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein | Nature Communications
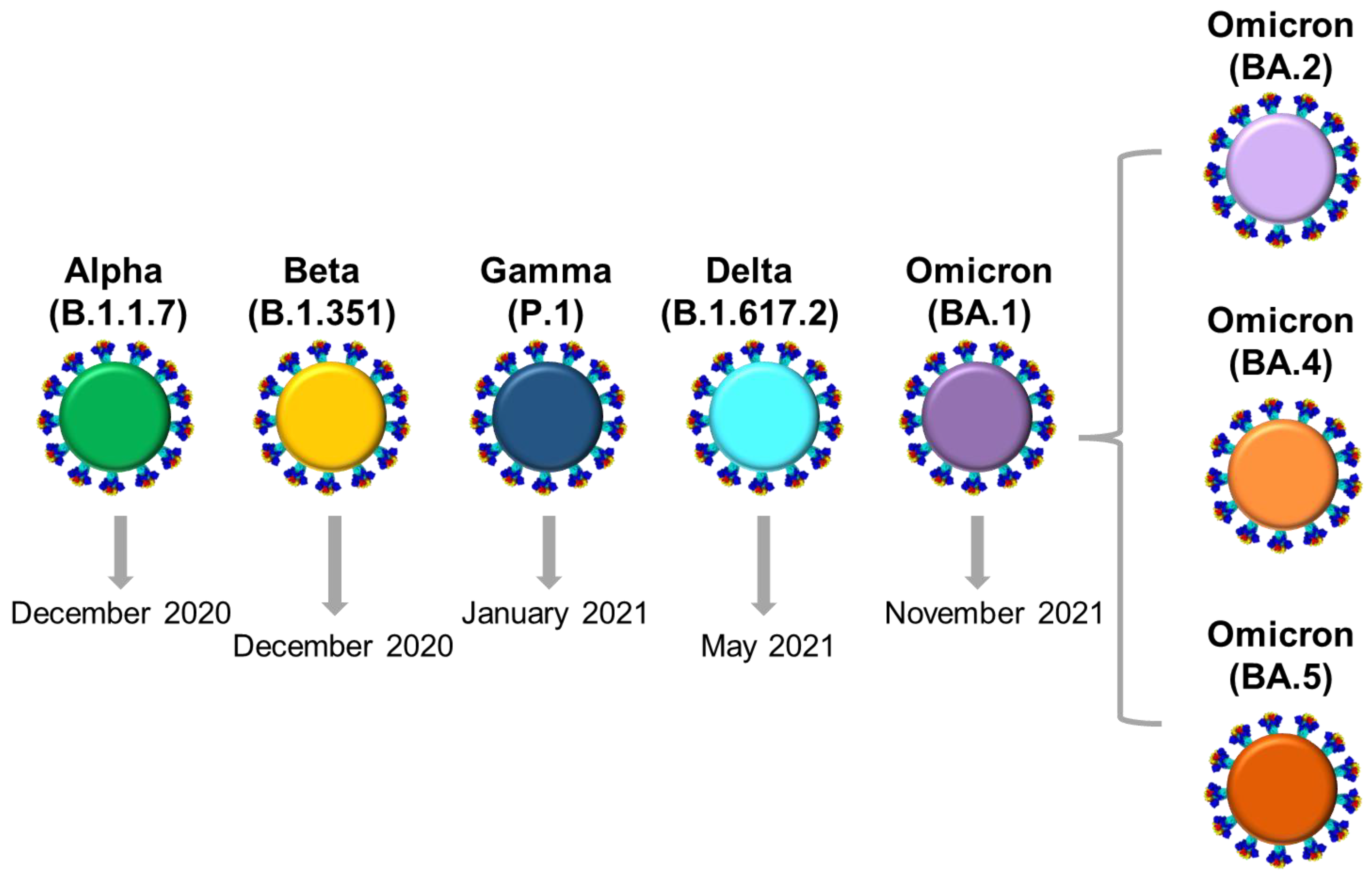
Life | Free Full-Text | Detection of Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOCs) Using a Multiallelic Spectral Genotyping Assay
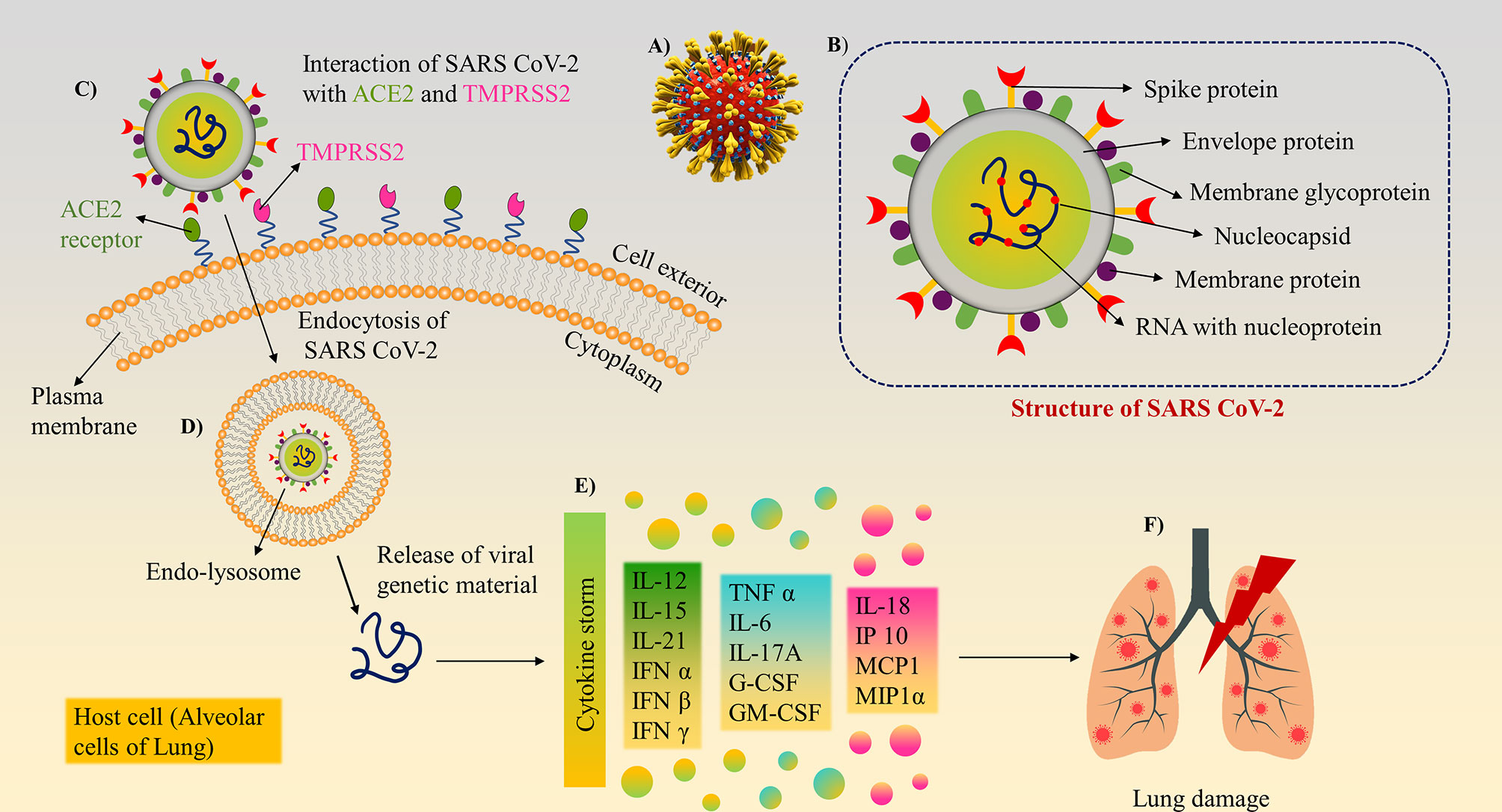
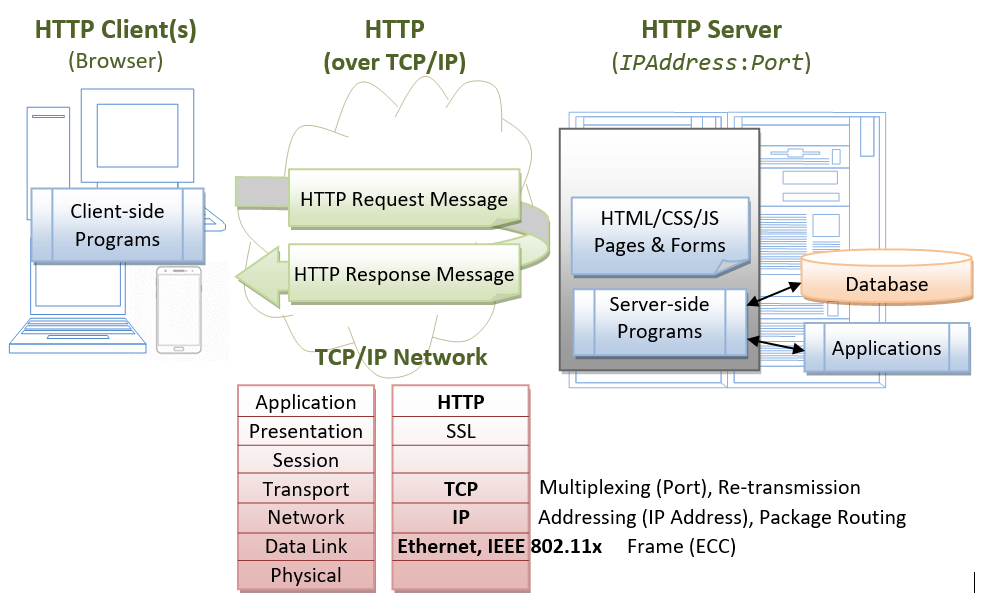
Frontiers | A Recent Update on Advanced Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview
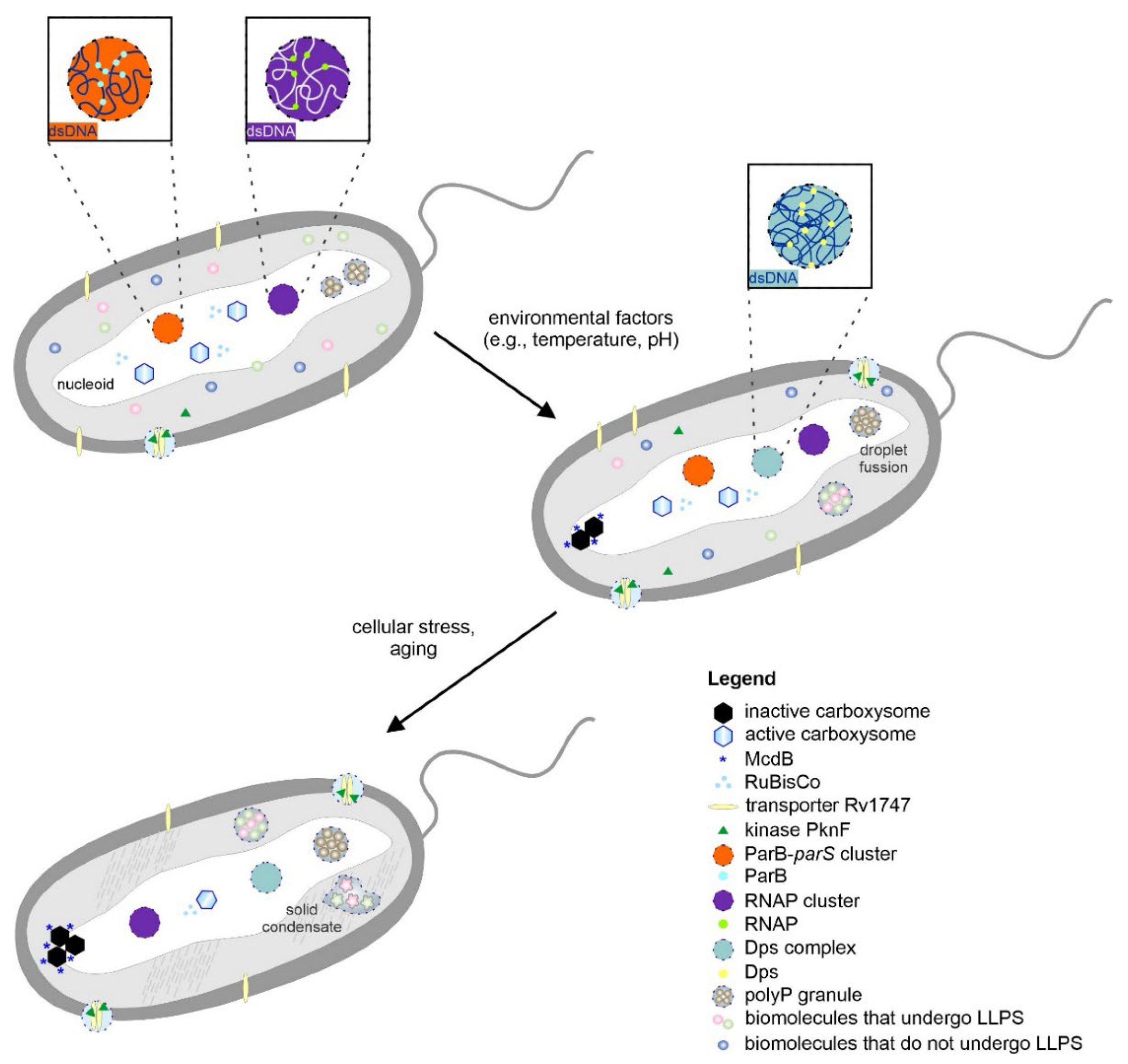
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Getting Closer to Decrypting the Phase Transitions of Bacterial Biomolecules

Detection of Metabolite–Protein Interactions in Complex Biological Samples by High-Resolution Relaxometry: Toward Interactomics by NMR | Journal of the American Chemical Society