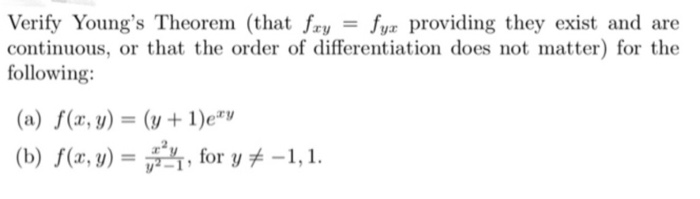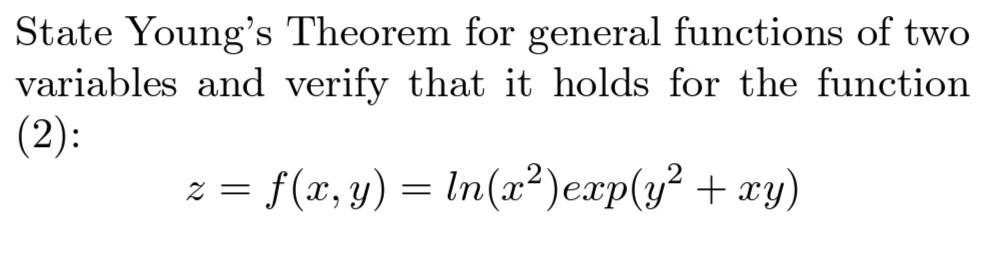Discovering the Mathematical Mind of Albert Einstein: The Fascination with Geometry and the Pythagorean Theorem
![SOLVED: 5. Let f(u,v) e2cos(u)+3v2 Verify Young's Theorem by showing that 244 82 f duav Ovdu [5 marks] 6 Show that f(z,y) is a homogeneous fUnction What is its degree? Ity Verify SOLVED: 5. Let f(u,v) e2cos(u)+3v2 Verify Young's Theorem by showing that 244 82 f duav Ovdu [5 marks] 6 Show that f(z,y) is a homogeneous fUnction What is its degree? Ity Verify](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/979ca2e3e3ce484f9cca36fda64d32ee.jpg)
SOLVED: 5. Let f(u,v) e2cos(u)+3v2 Verify Young's Theorem by showing that 244 82 f duav Ovdu [5 marks] 6 Show that f(z,y) is a homogeneous fUnction What is its degree? Ity Verify
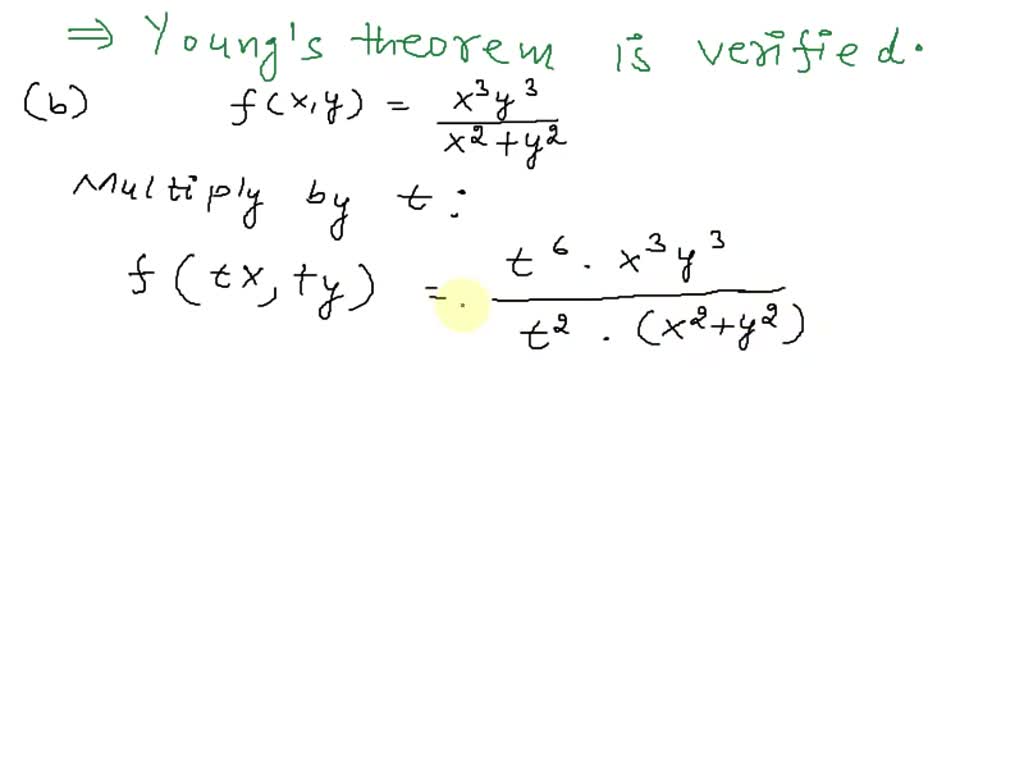
SOLVED: (Euler' Theorem) A funetion f(T,y) is said to be homogeneous of degree p if f(tr,ty) tf(1,y) for all real numbers t. Show that any differentiable and homogeneous function of degree p

An Analysis of the First Proofs of the Heine-Borel Theorem - Young's Proof | Mathematical Association of America

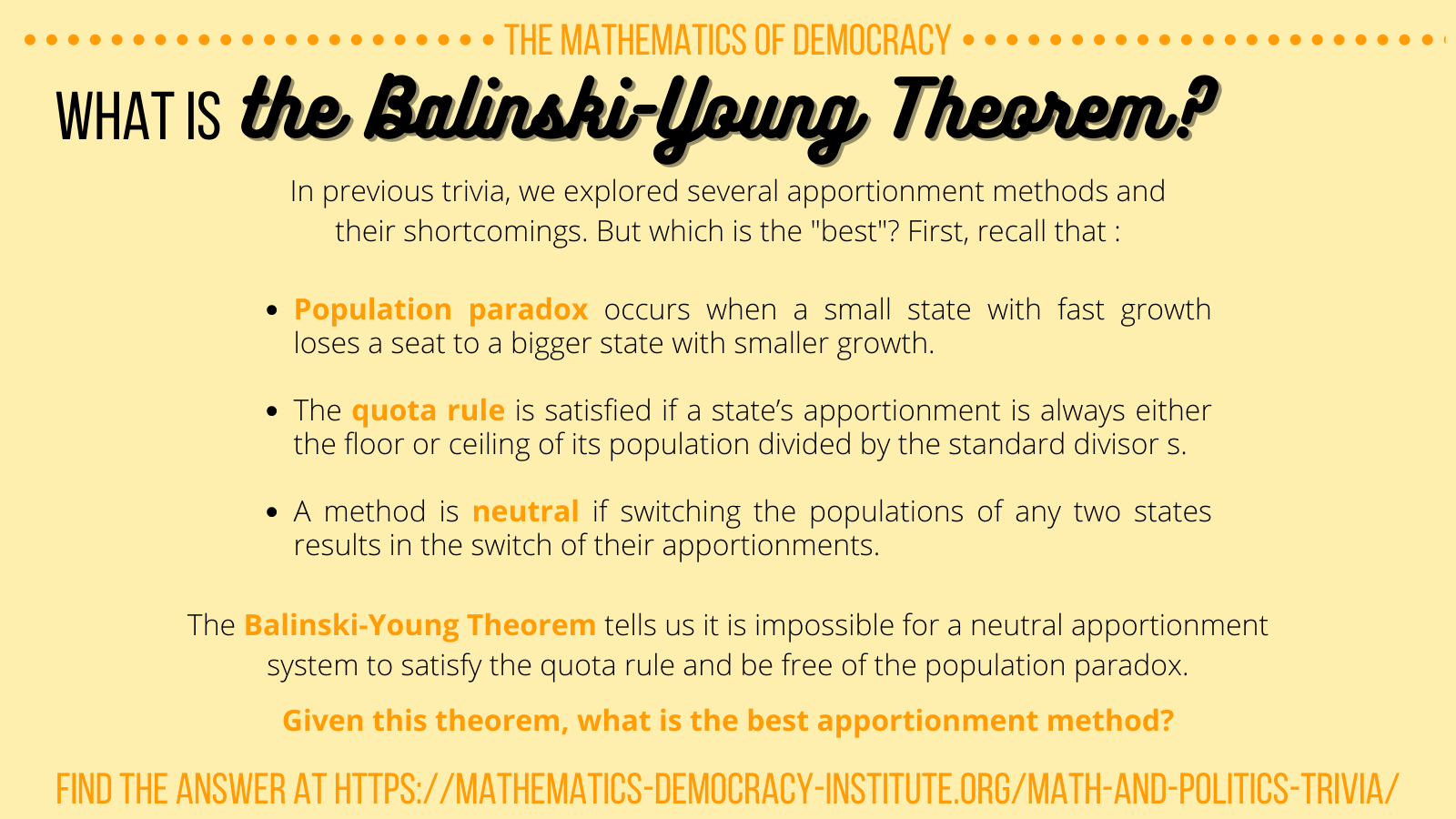
Chapter 15: Apportionment Part 7: Which Method is Best? Paradoxes of Apportionment and Balinski & Young's Impossibility Theorem. - ppt download